Introduction
Within the standard model of particle physics, particles and their antiparticles are predicted to have exactly the same modulus of charge, mass, lifetime and g-factor as a result of CPT invariance (invariance under time reversal, charge conjugation and spatial inversion). In the QLEDS project (Quantum Logic Enabled Test with Discrete Symmetries), we are developing techniques for quantum logic inspired cooling and detection of single (anti-)protons. These techniques are aimed at a test of CPT invariance based on the (anti-)proton's magnetic moment which is currently under development with the BASE collaboration (Baryon-Antibaryon Symmetry Experiment).
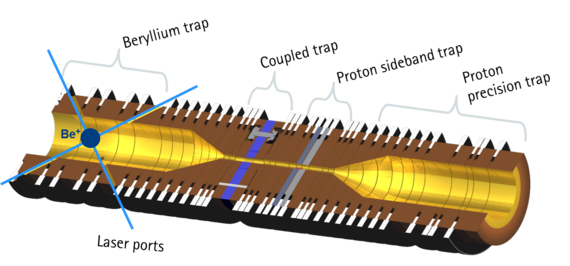
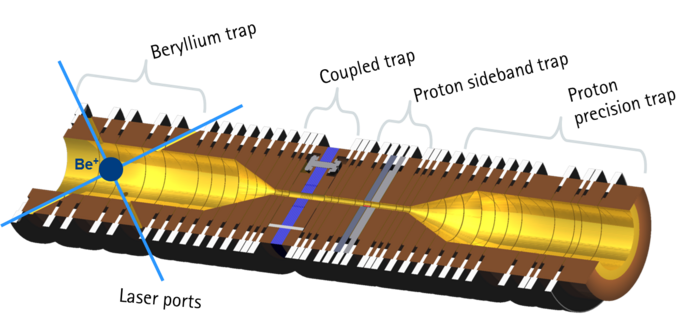
This quantum logic inspired approach had been proposed by D. Heinzen and D. J. Wineland in 1990 [1, 2]. The basic idea is to couple the (anti-)proton to an atomic "qubit" ion trapped in its vicinity via the Coulomb interaction and to exploit this coupling both for ground state cooling of single (anti-)protons as well as for state readout. This project uses some of the same techniques as our project on quantum logic in microtraps to achieve the desired coupling between the qubit ion and the (anti-)proton. Compared to our quantum logic surface-electrode traps, this project will employ a miniaturized Penning trap in a 5 Tesla superconducting magnet.

References
- [1] D. J. Heinzen and D. J. Wineland, Phys. Rev. A, 42 (1990)
- [2] D. J. Wineland et al., J. Res. NIST, 103, 259 (1998)


